« Immunosuppressive drugs are responsible for treatment failure in up to
40% of cases
in chronic inflammation. »
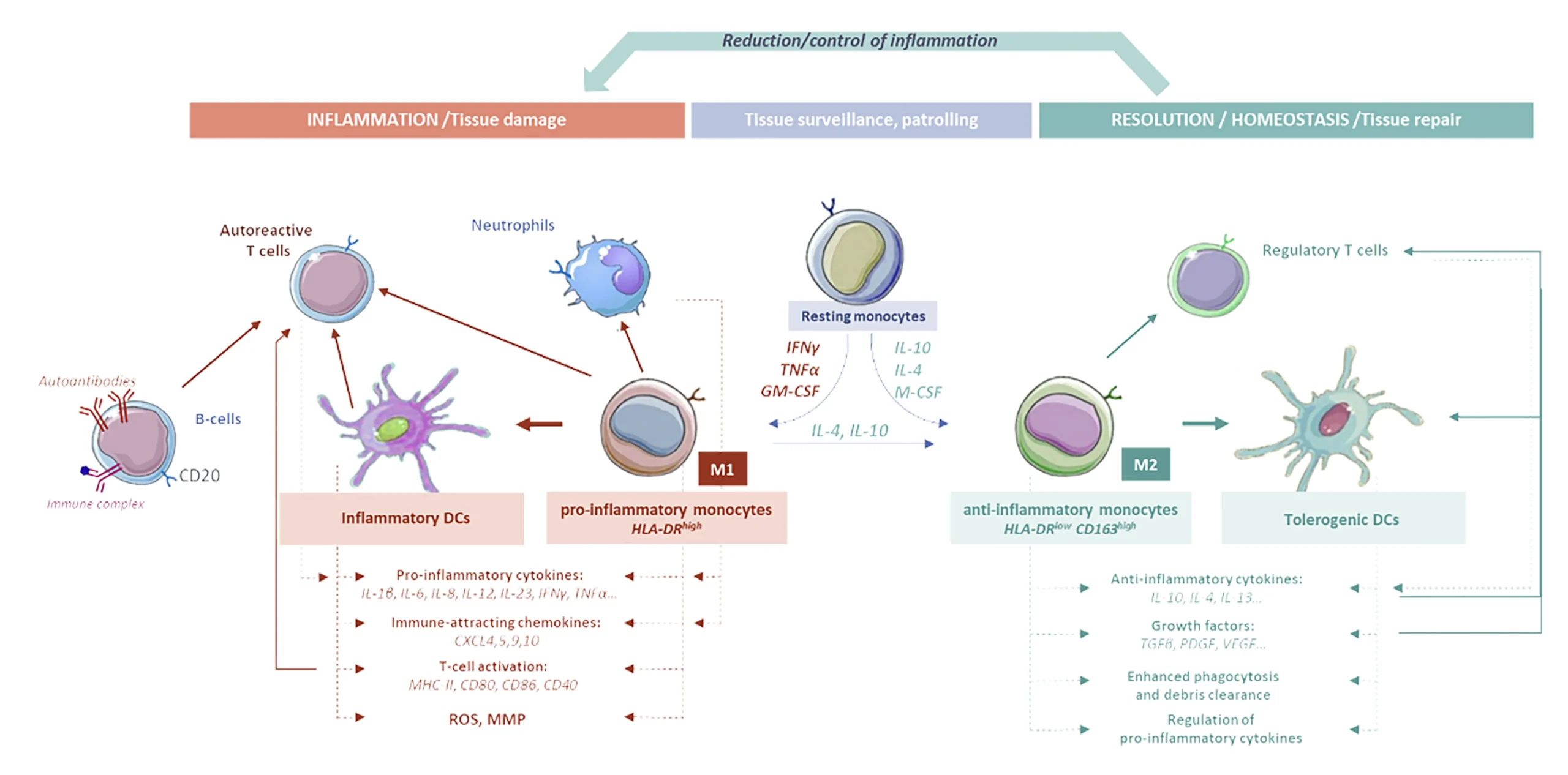
Chronic Inflammatory Diseases (CIDs) are characterized by a dysregulation of the immune system responsible for a long and persistent inflammation that can affect multiple organs or body parts. 1% of the world’s population is diagnosed with a CID.
Although the causes of CIDs are only partially documented and uncertain, they are all characterized by a malfunction of the immune system, which is no longer “in balance”: it produces more pro-inflammatory signals than pro-resolutive signals.
This dysregulation is highly complex, involving many different cell types, molecular messages and redundant signaling pathways, and monocytes play a central role in both the pro-inflammatory response and the anti-inflammatory (pro-resolutive) response.
For almost three decades, treatments have been relying on immunosuppressive therapeutic strategies using drugs that are generally repurposed from oncology-related R&D programs, like biologics, antineoplastic drugs or kinase inhibitors.
These immunosuppressive therapeutic strategies do not rebalance patients’ dysregulated immune systems: their limited efficacy and the adverse effects they produce are responsible for treatment failure in up to 40% of cases.

For almost three decades, treatments have been relying on immunosuppressive therapeutic strategies using drugs that are generally repurposed from oncology-related R&D programs, like biologics, antineoplastic drugs or kinase inhibitors.
These immunosuppressive therapeutic strategies do not rebalance patients’ dysregulated immune systems: their limited efficacy and the adverse effects they produce are responsible for treatment failure in up to 40% of cases.

Committed to discovering novel pathways to address unmet medical needs in chronic inflammatory diseases

Rémy and Cédric-Olivier have conceived, developed and validated a new chemical space from which several proprietary chemical platforms have originated (IMD-006, IMD-026, IMD-036…).
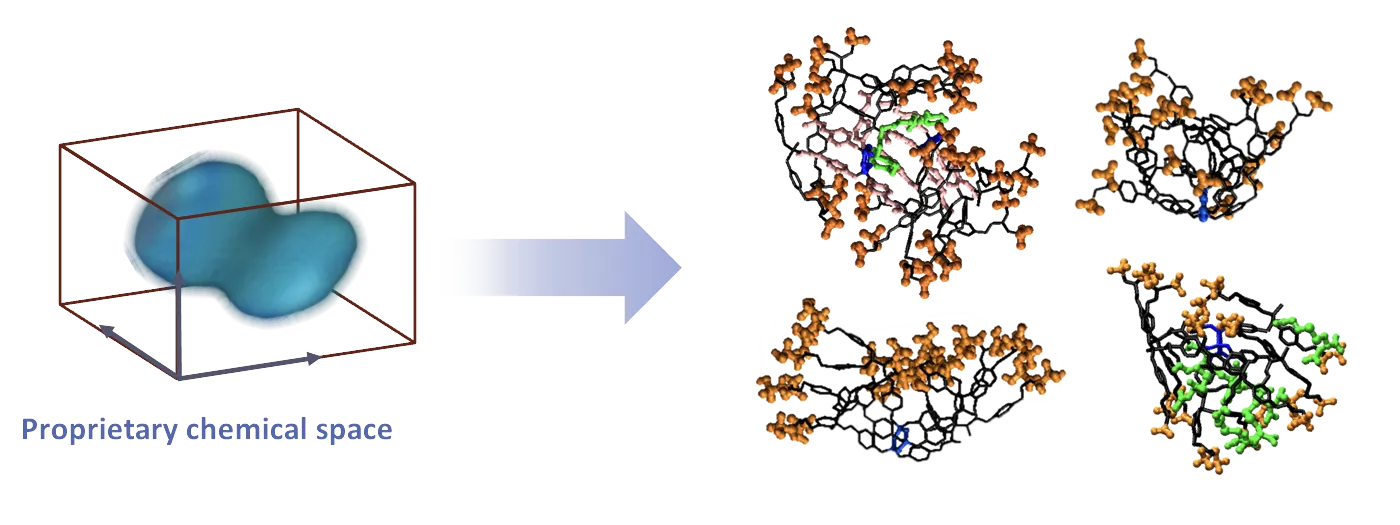
Whereas most marketed immunosuppressive anti-inflammatory drugs (conventional or biologic) interact with a single molecular target (receptor). IMD-Pharma’s drug candidates, thanks to their size and multivalent features, interact with a pool of receptors that are highly relevant to CIDs with KDs in the nanomolar range.
This new mode of action is more efficient and resolves inflammation through rehabilitation of several key immune cells with far less adverse effects in murine and non-human primate models. IMD-Pharma’s team has identified drug interactions with key molecular and cellular actors involved in CIDs. For instance, specific interaction with multiple receptors on monocytes, leading to their orientation towards an anti-inflammatory phenotype. CD4+ T lymphocytes are also rebalanced by IMD-Pharma’s drug candidates: the IL-2 driven proliferation of CD4+ T cells is specifically inhibited by decreasing the expression of CD25 (IL-2 receptor) while the proliferation of IL-10 producing T cells is triggered.
Non clinical studies – POCs

Rheumatoid Arthritis
Proof of efficacy in IL-1ra KO and K/BxN mouse models. Data on RA patient’s biopsies.
Anti-inflammatory and antiosteoclastic activities.
Suppression of disease is characterized by normal synovial membranes, reduced levels of inflammatory cytokines, and the absence of cartilage destruction and bone erosion.

Psoriasis
Proof of efficacy IMQ-induced psoriatic mouse model in the absence of formulation. Topical application enables the control of the clinical and histopathological scores. IMD-006 controles of the infiltration of macrophages in the skin of treated mice.
Data on formulation efficiency is unpublished.
Neuro-inflammation
Proof of efficacy in MOG35–55-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mouse model. IMD-006 reduces neuroinflammation by promoting IL-10 producing CD4+T lymphocytes. IMD-0006 inhibits the progression of established disease with a comparable therapeutic benefit as the approved treatment Fingolimod.
About directionnality
Dendrimers are highly branched macromolecules in which the surface function and the way they are spatially arranged play a crucial role when considering biomedical applications.

Immuno-Safety
IMD-006 was administered IV (10 mg/Kg/week, 4 injections) in healthy non-human primates to detect early toxicity and potential immunosuppression. No adverse response was detected (clinical observation, biochemical and hematological monitoring, cytokine profiling…).

Preclinical derisking
On the way to clinical translation, this article compiles early non-clinical data on IMD-006: biodistribution, hematological safety, immunosafety, genotoxicity, maximal tolerated doses, and early cardiac safety…
Let’s get in touch
Cédric-Olivier Turrin
+33 (0)6 48 16 85 39
IMD-Pharma S.A.S.
205 route de Narbonne (LCC-CNRS)
31077 Cedex 4
FRANCE